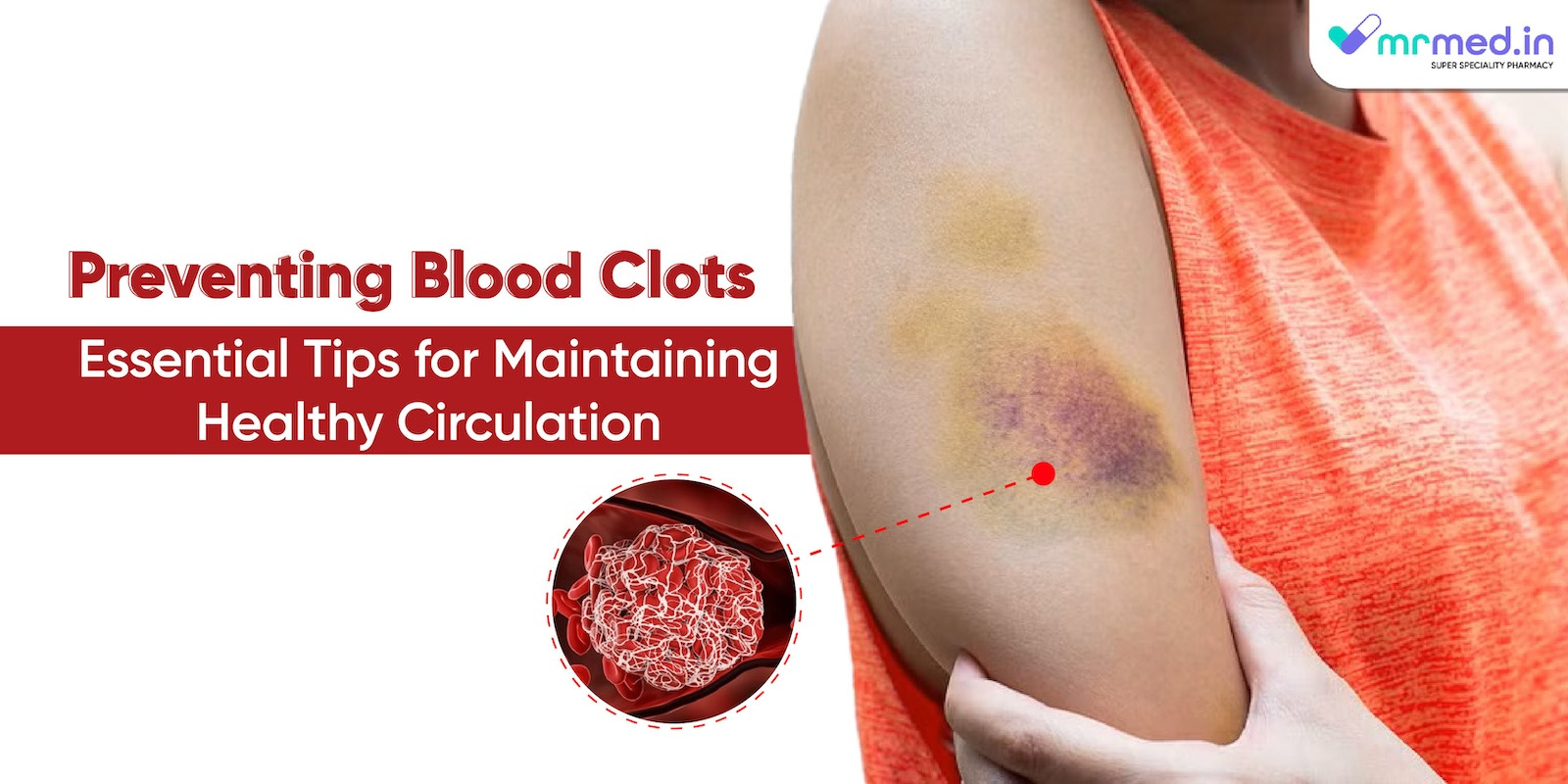
Blood clots are a serious health concern that can lead to life-threatening conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism. Maintaining healthy circulation is crucial for preventing these dangerous clots. By understanding the risk factors and implementing preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of developing blood clots.
What is the root cause of blood clots?
Blood clots form when blood thickens and clumps together. While clotting is a natural process that stops bleeding, abnormal clot formation can block blood flow and cause severe complications. Deep vein thrombosis, which occurs when a clot forms in a deep vein (usually in the legs), is a common and dangerous type of blood clot.
Recognising the Signs of Blood Clots
Early recognition of blood clot symptoms can lead to prompt treatment and prevent complications. Common signs include:
- Swelling: Unexplained swelling in the leg, especially if accompanied by pain, redness, or warmth.
- Pain: Sudden and severe pain in the leg or calf that worsens with movement.
- Breathlessness: Shortness of breath, chest pain, or rapid heartbeat, which may indicate a pulmonary embolism.
What are the risk factors for thrombosis?
Several factors can increase the risk of blood clots, including:
- Prolonged Immobility: Extended periods of inactivity, such as long flights, car rides, or bed rest, can slow blood flow, significantly increasing the risk of blood clots.
- Post-Surgical Recovery: Surgery, particularly involving the legs, hips, or abdomen, can lead to prolonged immobility and heightened blood clot risk during recovery.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer and chemotherapy treatments can increase the likelihood of clot formation due to changes in blood properties and reduced mobility.
- Heart Disease: Cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease and atrial fibrillation, can disrupt normal blood flow and elevate the risk of clotting.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly obesity, reduces blood flow and increases pressure in the veins, raising the risk of clots.
- Medications: Certain medications, including hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptives, and anticoagulant medicines like Clexane 60mg Injection, can influence clotting tendencies.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and alters blood properties, making smokers more susceptible to blood clots.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity can lead to poor circulation and an increased risk of clot formation, especially in the lower extremities.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can cause blood to thicken, making it more prone to clotting, especially during periods of prolonged inactivity.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of blood clotting disorders, such as Factor V Leiden mutation, can predispose individuals to a higher risk of developing clots.
What promotes good blood circulation?
Implementing preventive measures can help maintain healthy circulation and reduce the risk of blood clots. Here are some essential tips:
1. Stay Active
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to maintain healthy circulation. Exercise promotes blood flow and helps prevent clot formation. Activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling are excellent options. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
2. Hydrate Properly
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining optimal blood viscosity. Dehydration can thicken the blood and increase the risk of clots. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps keep the blood flowing smoothly and reduces clotting risk.
3. Manage Weight and Diet
Maintaining a healthy weight and eating a balanced diet are essential for preventing blood clots. Excess body weight, particularly obesity, increases the risk of DVT. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health and circulation.
4. Role of Anticoagulant Medicines
Anticoagulant medicines, also known as blood thinners, play a critical role in preventing and treating blood clots. These medications work by inhibiting the clotting process, thereby reducing the risk of clot formation.
Anticoagulants interfere with the body's natural clotting mechanisms. Enoxaparin, for example, is a low molecular-weight heparin that inhibits certain clotting factors, preventing the formation of new clots and the growth of existing ones. This medication is often prescribed for individuals at high risk of DVT or those undergoing surgery.
How can blood clots be prevented?
In addition to the above measures, consider the following tips to reduce the risk of blood clots further:
1. Elevate Legs
Elevating the legs periodically can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of clot formation, especially during long periods of sitting or lying down.
2. Wear Compression Stockings
Compression stockings are specially designed to promote blood flow in the legs and reduce the risk of DVT. They are particularly beneficial for individuals who spend extended periods on their feet or are prone to swelling.
3. Avoid Prolonged Inactivity
During long journeys or periods of immobility, make an effort to move around periodically. Simple exercises like ankle rotations, leg lifts, and short walks can help keep the blood flowing.
4. Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups allow healthcare providers to assess clotting risks and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Monitoring conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol is crucial for maintaining healthy circulation.
5. Medication Adherence
For individuals prescribed anticoagulant medicines or other treatments, adhering to medication regimens is vital. Skipping doses or discontinuing medication without medical advice can increase the risk of clot formation.
Conclusion
Regular physical activity, proper hydration, a balanced diet, and the safe use of anticoagulant medicines play crucial roles in this endeavour. Staying vigilant and proactive in managing health conditions and recognising early symptoms can further enhance one's ability to prevent blood clots and maintain optimal health.