Key Takeaways
- Pneumonia can be viral or bacterial, and the cause guides treatment.
- Viral pneumonia develops gradually and is usually milder.
- Bacterial pneumonia starts suddenly and is often more severe.
- Treatment differs, supportive care for viral and antibiotics for bacterial.
- Vaccination and early care lower the risk of complications.
Pneumonia is often spoken about as if it is a single illness, but in reality, it comes in different forms. The most common source of confusion is between viral and bacterial pneumonia. Both affect the lungs, both can make breathing difficult, and both can feel frightening, especially when symptoms worsen quickly. Understanding the difference helps people know what to expect and why treatment plans may vary.
Let us break this down in a clear, everyday way.
What Is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammatory illness of the air sacs (alveoli) in your lungs, caused by infection with bacteria, viruses or fungi (rarely), which subsequently fill the alveoli with fluid or pus. The inflammation fills the alveoli with fluid and pus, making it more difficult for the body to take in oxygen and resulting in reduced oxygen levels.
The type of pathogen responsible for pneumonia will largely determine the severity of the illness and the methods utilised to treat it.
What Is Viral Pneumonia?
Viral pneumonia is caused by viruses that are responsible for the flu or common respiratory infections.
Common Features of Viral Pneumonia
- Symptoms often start slowly
- Fever is usually mild to moderate
- A dry cough is common
- Body aches and fatigue are more noticeable
- Breathing difficulty may develop gradually
Viral pneumonia is often seen after a viral cold or flu. In many healthy individuals, it can improve with rest and supportive care, though some cases may still become serious.
What Is Bacterial Pneumonia?
Bacteria cause bacterial pneumonia and tend to be more aggressive.
Common Features of Bacterial Pneumonia
- Sudden onset of symptoms
- High fever with chills
- Productive cough with yellow or green mucus
- Sharp chest pain while breathing or coughing
- Faster worsening of symptoms
Bacterial pneumonia often requires prompt medical treatment, as it can progress quickly and lead to complications if delayed.
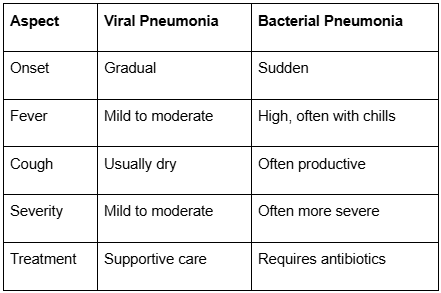
Key Differences Between Viral and Bacterial Pneumonia
How Treatment Differs
Treatment depends entirely on the cause.
- Viral pneumonia usually improves with rest, fluids, fever control, and monitoring
- Bacterial pneumonia requires antibiotics prescribed by a doctor
Because symptoms can overlap, doctors may use blood tests, chest X-rays, or other investigations to confirm the cause before starting treatment.
Role of Vaccination in Pneumonia Prevention
Through immunisation, certain forms of pneumonia may be prevented.
One particular vaccine, Prevenar 13, which contains the Pneumococcal Vaccine, was designed to protect against the bacteria that cause Pneumonia (i.e., Pneumococcus). Pneumococcal Pneumonia is one of the common types of bacterial Pneumonia seen in young children, the elderly, and those with chronic medical conditions.
Although vaccination cannot prevent all types of pneumonia, it reduces the risk of severe illness and pneumonia-related complications in at-risk or susceptible populations.
Recovery Time and What to Expect After Pneumonia
The length of time it takes to recover from pneumonia can vary by individual and depends on their overall health, age, and the cause of the illness.
- Viral pneumonia usually improves within 1-2 weeks, but fatigue may linger for longer.
- Individuals with bacterial pneumonia may take 4-8 weeks to recover fully after starting treatment.
- Coughing and weakness may persist after the fever has resolved.
Because the body requires time to heal, patients should make sure they are getting enough rest, nutrition and continued follow-up with their healthcare provider before returning to normal activities.
Who Is at Higher Risk of Severe Pneumonia?
No one is immune to pneumonia; however, the following populations are considered at greater risk.
- Children aged five years or younger
- Older adults (aged greater than sixty)
- Individuals with chronic health conditions such as asthma, diabetes and heart disease.
- Individuals who are immunocompromised.
If these groups experience symptoms of pneumonia, they are strongly encouraged to seek prompt medical attention.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Medical attention is needed if pneumonia symptoms include:
- High or persistent fever
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Confusion or extreme weakness
Early diagnosis improves recovery and reduces complications.
Final Thoughts
Viral and bacterial pneumonia may sound similar, but they behave differently and require different approaches to care. Viral pneumonia often improves with time and supportive care, while bacterial pneumonia usually requires timely antibiotic treatment. Knowing the difference helps patients and families understand why doctors make certain decisions and why prevention, including vaccination, plays such an important role in reducing the risk of serious illness.