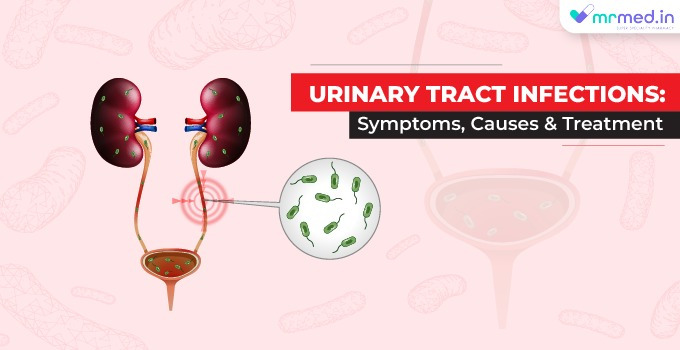
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a common bacterial infection caused by bacteria from the digestive system that enters the urethra and travels up into the bladder or other parts of the urinary system. The urinary tract comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It can occur in any part of the urinary tract, but most commonly affect the bladder and urethra. UTIs are more common in women than men, women experiencing at least one UTI during their lifetime. This is due to the shorter urethra in women, which makes it easier for bacteria to travel up to the bladder.
Common symptoms of UTI:
- Burning sensation during urination
- Frequent or intense urge to urinate
- Blood in the urine
- Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back
Causes of UTI:
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria, with Escherichia coli (E. coli). Other bacteria that can cause UTIs include Klebsiella, Proteus, and Enterococcus.
Factors that can increase the risk of UTI include:
- Diabetes
- Kidney stones
- Using certain types of birth control (such as diaphragms or spermicidal agents)
- Menopause
- Being sexually active
- A weakened immune system
Diagnosis of UTI:
Urinalysis is a common laboratory test used to diagnose UTIs. It involves examining a sample of urine under a microscope to detect the presence of white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria. A urine culture may also be performed to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Treatment for UTI:
Fosfomycin is a newer antibiotic drug which helps to treat uncomplicated UTIs. It involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Mainly, urinary infections are treated with antibiotics, which can be prescribed by a doctor based on the type of bacteria causing the infection and the patient’s medical history. Some commonly prescribed antibiotics for UTIs are listed below,
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole: This is a combination antibiotic that is effective against many types of bacteria commonly found in UTIs.
- Nitrofurantoin: It is often used to treat uncomplicated UTIs caused by certain types of bacteria.
- Ciprofloxacin: This antibiotic is effective against a wide range of bacteria and may be used to treat more complicated UTIs or infections that have spread to the kidneys.
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate: It is an antibiotic drug used to treat UTIs caused by resistant bacteria(Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus).
In addition, drinking plenty of water and urinating frequently can help to flush out the bacteria from the urinary tract. If left untreated, UTIs can lead to more serious complications such as kidney infection or sepsis. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you may have a UTI.
Patient counselling for UTI:
- Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help flush out the bacteria causing the infection.
- Taking antibiotics as prescribed and completing the full course of treatment is important to ensure that the infection is completely suppressed.
- Keeping the genital area clean and dry, wiping from front to back after using the toilet, and avoiding irritating products can help prevent UTIs.
- Urinating before and after sexual activity, using condoms, and spermicidal products also reduce the risk of UTIs.
Fosirol powder is an antibacterial drug, which contains the active ingredient Fosfomycin Trometamol. It is prescribed to treat uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. It is also indicated for the prevention and treatment of bladder infections. This medication works by inhibiting the bacterial cell wall synthesis, which leads to cell death of the bacteria causing the infection. Headache, dizziness, indigestion, fast heart beat, diarrhoea are some of the common side effects of the Fosirol Powder.