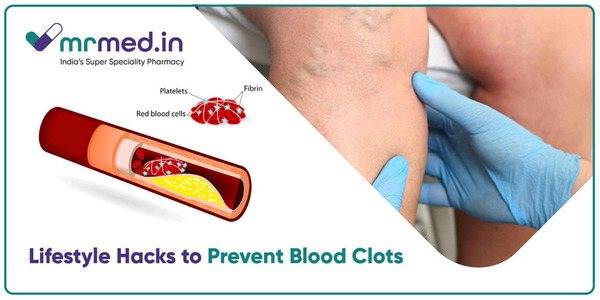
Blood clots are more than just an inconvenience; they can result in serious health complications such as stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism if left unchecked. In many cases, these clots form when blood flow is disrupted or slowed down, creating a risk for blockages in the veins or arteries.
However, preventing blood clots is possible with the right lifestyle changes. By focusing on physical activity, diet, hydration, and other habits, you can significantly lower your risk and safeguard your health.
Who is at risk for developing blood clots?
Some factors increase the risk of developing blood clots. Understanding these risks can help in making preventive lifestyle changes. Key risk factors include:
- Prolonged inactivity: Long periods of sitting, such as during flights or car rides, slow circulation.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on veins, hindering circulation.
- Smoking: Harms blood vessels and decreases oxygen levels, increasing clot risk.
- Chronic conditions: Heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure affect blood flow and vessel health.
- Genetic factors: Inherited clotting disorders can make individuals more prone to clots.
- Recent surgery: Surgeries, particularly involving the legs or hips, can disrupt blood flow.
What are the lifestyle changes to prevent blood clots?
Understanding these risks helps in making proactive changes that can prevent clot formation before it becomes a problem.
1. Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is key to reducing blood clot risk by promoting healthy circulation. Exercise keeps blood flowing and prevents clot formation, particularly in the lower extremities.
- Weight-bearing exercises: Walking, cycling, and swimming improve circulation.
- Movement for limited mobility: Simple leg lifts or ankle pumps stimulate blood flow.
- Frequent breaks: For desk jobs, stand up, stretch, or walk every 30-60 minutes to lower the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Staying active helps keep your veins functioning properly and reduces clotting risk.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity increases the risk of blood clots by placing excess pressure on veins and slowing circulation, but even modest weight loss can significantly reduce this risk by improving blood flow.
- Balanced diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Avoid processed foods: Minimize unhealthy fats, sugars, and salt, which contribute to inflammation.
- Weight management: Losing weight reduces pressure on veins and improves circulation.
3. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration thickens the blood, raising the risk of clots, so staying hydrated is essential to maintaining healthy circulation and preventing blood from becoming viscous, which can impede blood flow. Proper hydration helps maintain smooth blood flow and reduces clotting risk.
- Water intake: Try to drink 8-10 glasses of water daily, more if active or in hot climates.
- Balance beverages: Drink water alongside caffeine or alcohol, which can dehydrate the body.
- Variety: Herbal teas or fruit-infused water offer refreshing alternatives while keeping you hydrated.
4. A big NO to smoking
Smoking greatly raises the risk of blood clots by damaging blood vessels and reducing oxygen levels in the blood, which promotes clot formation. Quitting smoking improves circulation and lowers your clotting risk. Taking steps to quit or reduce smoking can greatly enhance your vascular health.
- Quit support: Seek help through counselling, nicotine replacement therapies, or cessation programs.
- Immediate benefits: Even reducing smoking can improve circulation and health.
- Health improvement: Quitting smoking significantly lowers the risk of clot formation and cardiovascular issues.
5. Wear Compression Stockings
For individuals at high risk of blood clots—such as those who have undergone surgery or frequently travel long distances—compression stockings can be a helpful preventative measure. These stockings involve gentle pressure on the legs, stimulating blood flow and stopping blood from pooling in the veins. Wearing the right compression stockings can help decrease the risk of clot formation by enhancing circulation.
- Types and sizes: Compression stockings come in various strengths and sizes to suit individual needs.
- Consult a healthcare provider: Seek professional advice to choose the correct compression level.
- Post-surgery use: They are especially beneficial for post-surgery recovery or long periods of immobility.
6. Modify Your Diet
Certain foods can naturally help reduce the risk of blood clot formation by promoting healthy blood flow and reducing inflammation. Including these in your diet can support overall vascular health.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines reduce inflammation and improve circulation.
- Vitamins C and E: Citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds maintain healthy blood vessels and protect against clot formation.
- Garlic: Known for its ability to inhibit platelet aggregation, reducing clot risk.
- Vitamin K moderation: Foods like kale and spinach are high in Vitamin K, which may interfere with blood-thinning medicines. Balance these foods if on medication.
Including these foods in your diet can help support your cardiovascular system while reducing clotting risks.
7. Monitor and Manage Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, can raise the risk of blood clots. Managing these conditions is essential to reducing strain on your cardiovascular system and lowering clotting risk.
- Regular check-ups: Monitor your health conditions through regular visits to your healthcare provider.
- Medication: Follow prescribed treatments to manage blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels.
- Lifestyle changes: Adopt a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management to support cardiovascular health.
In some cases, doctor providers may recommend medications to prevent clots. For example, the Clexane 40mg injection, containing Enoxaparin, helps prevent blood clots in high-risk individuals, such as those recovering from surgery or experiencing immobility. Always consult your healthcare provider for the best approach tailored to your needs.
8. Be Mindful During Long Trips
Long periods of immobility, like during flights or car rides, increase the risk of blood clots. To reduce this risk, follow these tips:
- Stay active: Walk or stretch regularly.
- Compression stockings: Help maintain circulation.
- Comfortable clothing: Wear loose-fitting attire.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent blood thickening.
These measures can help keep circulation healthy and reduce clot risk during travel.
Wrapping up
Preventing blood clots doesn’t require drastic measures—small, consistent lifestyle changes can significantly influence your overall vascular health. Regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking are all excellent strategies for keeping your blood flowing smoothly and reducing the risk of clot formation.
By adopting these habits, you can significantly lower your chances of experiencing the potentially life-threatening effects of blood clots, helping you lead a longer, healthier life.